After reaching out to more than 500 enterprises, the results are clear. The large language model (LLM) competition is fierce, with a few dominant players leading the charge and others carving out specialized niches (see below exhibit).
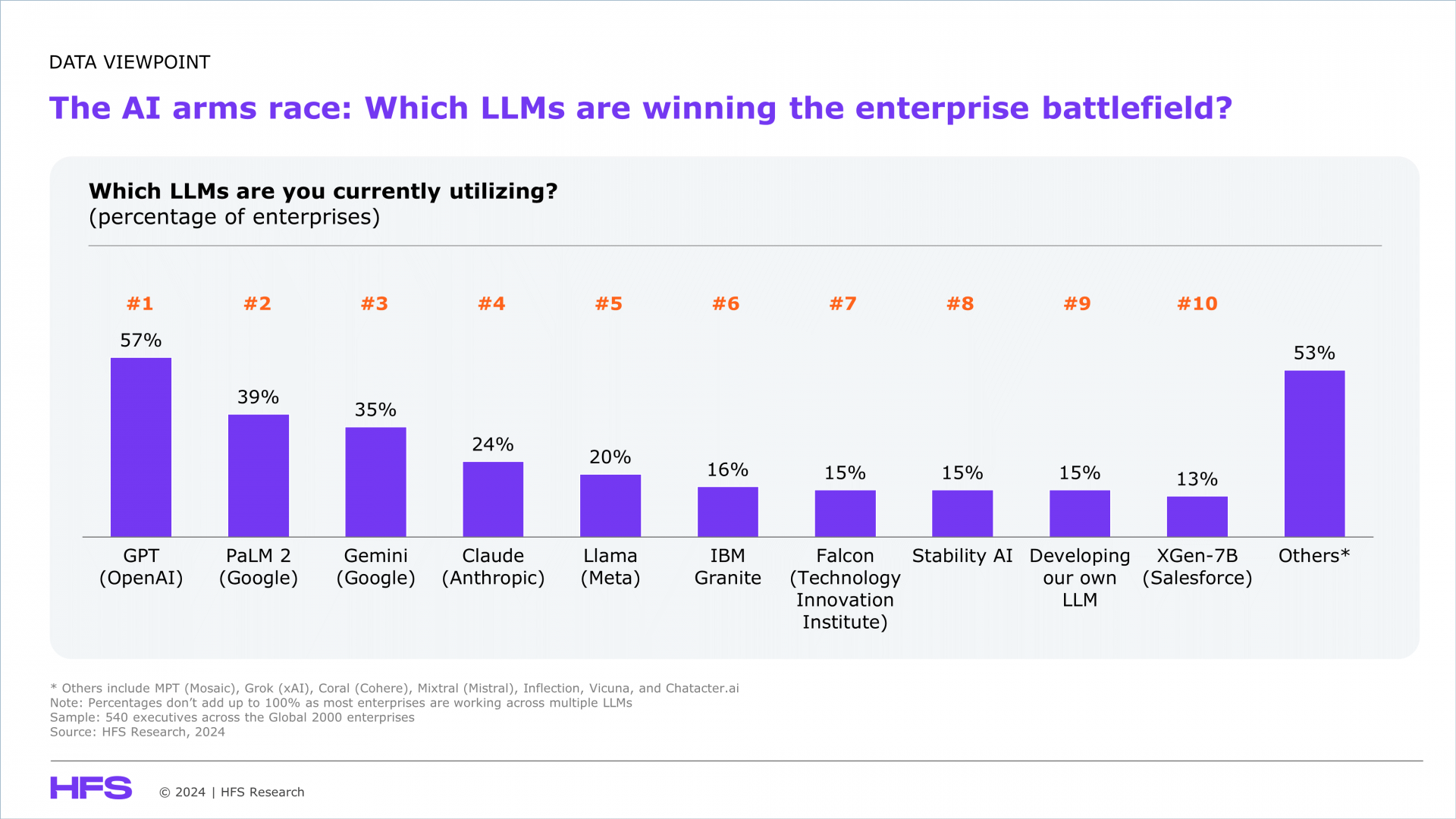
Here’s the breakdown, including insights on open-source options that are gaining ground:
- GPT (OpenAI) leads by a landslide: With a massive 57% adoption rate, OpenAI’s GPT is the go-to model for businesses, clearly owning the market. Its versatility and performance have set a high bar that competitors are struggling to match. However, as a proprietary model, it’s primarily accessible through licensing, giving open-source models an edge in customization.
- Google’s double play with Gemini and PaLM 2: Google’s models are no small threat, with Gemini achieving a 35% adoption rate and PaLM 2 at 39%, firmly positioning Google as a top contender. Both are proprietary, but Google’s market position and ecosystem integrations make it a competitive choice despite its closed nature.
- Open source rising (Llama, Falcon, and MPT): Llama (20%), Falcon (15%), and MPT (10%) stand out as open-source alternatives that are gaining ground. Open-source models offer companies customization capabilities, flexibility in deployment, and more control over data usage—a key draw for businesses with specific security or data compliance needs. Their accessibility especially appeals to enterprises looking to tweak and fine-tune models for specialized tasks.
- The rise of proprietary enterprise-focused models: While open-source options are gaining popularity, proprietary models such as IBM Granite (16%) also make strong showings, especially for enterprises that trust established brands for critical enterprise needs. These closed models cater to businesses needing structured, vendor-supported implementations over open-ended customization.
- Going solo—proprietary models on the rise: In a bold move, 15% of enterprises are bypassing third-party models altogether to develop their own LLMs. This approach reflects a growing trend toward customization and control, as companies seek AI solutions uniquely tailored to their goals.
- Low visibility for smaller players, but broad experimentation: Models like MPT (Mosaic), Grok (xAI), Coral (Cohere), Mixtral (Mistral), Inflection, Vicuna, and Chatacter.ai haven’t yet achieved widespread adoption, either due to limited feature sets or lack of mainstream enterprise appeal. However, over 50% of enterprises are experimenting with LLMs outside of the top 10 most popular choices—indicating a nascent stage and a healthy appetite for testing newer or specialized models that might fit niche requirements better.
The Bottom Line: The choice between open-source and proprietary LLMs closely mirrors the public versus private cloud debate.
Enterprises are weighing the flexibility and community-driven innovation of open-source models (similar to public cloud offerings) against the structure, support, and security of proprietary models—much like opting for private cloud environments. This dual trend in AI maturity underscores how enterprises should balance flexibility with structured support to drive competitive advantage—ushering in an exciting era.
